modshell
[!WARNING] The program is still under development, it is not yet suitable for its task.

Modshell
Command-driven scriptable Modbus utility
Copyright (C) 2023-2025 Pozsár Zsolt pozsarzs@gmail.com
About this project
This project started in December 2023 as a Christmas project, to wind down the busy end-of-year period.The original goal was to create a utility that would allow multiple Modbus devices of the same type to be configured without using a touchpad.
The project has grown considerably in size over time, but many features have been implemented that make it more useful. With the growth, the goal has also been reformulated: the program must have multiple user interfaces, be usable on many operating systems, handle multiple communication channels and protocols, be suitable for many tasks, and even work automatically.
The next goal is to create a field (installed) or handheld (mobile) data collector, converter, processor, etc., as well as a data and traffic monitoring device that works reliably, using this program, a single-board computer, and a mini HMI.
The choice of source language fell on the outdated and neglected FreePascal. Partly because of its multiplatform nature (‘Write once - compile everywhere’), partly because it is what I feel most comfortable with. I’m not sure it was the best choice, but you have to make the most of it.
The benefit of the project is not the finished product, as there are ‘thousands’ of similar products on the market. The biggest benefit is the development of logical thinking and the knowledge we gain while programming, but the greatest is the joy of creation. And this is not dependent on the programming language.
I. Features
ModShell is a utility built around a command interpreter, which with the connected peripherals communicates via various ports using the Modbus, DCON and HART protocols.
| features | |
|---|---|
| version | v0.1 |
| licence | EUPL v1.2 |
| language | en, hu |
| architecture | amd64, armhf, i386, x86_64 |
| operation system | DOS, FreeBSD, Linux, Windows |
| user interface | ModShell: CLI and TUI |
| XModShell: GUI | |
| running modes | normal or interpreter |
| variables | max. 128 variables or constants (stored as string) |
| arrays | max. 32 dynamic size array of variables or constants (elements stored as string) |
| built-in commands | 135 commands in 10 categories with macro and script options) |
| macros | max. 32 |
| script size | max. 1024 line |
| example scripts | 10 scripts (shellscript and batch file versions) |
| load from file | registers, script, settings |
| save to file | command history, console and Modbus traffic, registers, communication settings, user log |
| auto save to file | general settings and console traffic |
| export to file | history (TXT), registers (CSV, INI, XML) |
| import to file | registers (INI, XML) |
| configurable devices | max. 8 settings, serial and ethernet port |
| configurable protocols | max. 8 settings, ASCII, RTU or TCP |
| configurable connections | max. 8 settings by combining the previous two |
| raw serial communication | read/write serial port and mini serial console with A/N or Hex echo |
| raw TCP communication | read/write network device and mini TCP console with A/N or Hex echo |
| raw UDP communication | read/write network device and mini TCP console with A/N or Hex echo |
| DCON communication | read and write remote devices |
| HART communication | read and write remote devices |
| Modbus communication | read and write remote device and copy between devices |
| internal server for remote access to own registers | |
| gateway to access devices using other ports or protocols | |
| internal serial monitor for decode ASCII or RTU telegrams | |
| direct I/O port access | supported |
| GPIO port access | supported on IPC (max. 64 port) and Raspberry Pi version 1-4 |
| local Modbus registers | 2x9999 boolean and 2x9999 word type |
| script syntax plugins | for editors using GtkSourceView, MCEdit, Micro, Nano, Notepad++, (Neo)Vim and VSCode |
| utility scripts | 2 script |
| other utility programs | command line serial Modbus traffic monitor, serial, TCP and UDP echo servers |
II. Releases
Planned next releases up to v0.1
…that either will or won’t.
v0.1
This is first unstable release.Unstable, but it is already complete in its intended functionality. The software will not include any new features compared to the previous release, only bug fixes. All types of binary and installation packages will be released along with the source package.
v0.1-beta3
Third user test release will be with the following changes:- graphical monitoring the change of values over time (only XModShell);
- implementation of additional Modbus functions.
Actual release
0.1-beta2 Second user test release will be with the following changes:
- new command
abs; - new commands
gpioinit,gpioread,gpiowrite(Industrial PC and RaspberryPi GPIO port support); - new command
input; - new commands
pipe,stack; - new command
swp; - testscript directory for testing commands;
- compressed HTML (CHM) help in addition to the existing online Wiki (only XModShell);
- HART protocol support;
- Modbus/TCP communication;
- TCP/UDP communication on DOS;
- syntax highlighter and suggestion extension for Visual Studio Code.
Only a source package will be released.
Previous releases
v0.1-beta1
First user test release with the following changes:- Elimination of confusion between the terms 'register number' and 'data address'
- in interpreter mode, passing parameters from the OS command line to the script and returning the script's exit value to the OS
- in interpreter mode, command verbosity level setting with a predefined variable
- ANSI escape sequences support (only DOS and *nix like systems)
- command `color` -> `set color`, sets all default colors (CLI and TUI)
- command `echo` -> `echometh`, parameters: off/on/hex/swap -> off/an/hex/swap
- commands `sercons`, `tcpcons`, `udpcons`: character-to-character or string sending, with alphanumerical or hexadecimal input, with or without alphanumerical or hexhexadecimal echo
- commands `serwrite`, `tcpwrite`, `udpwrite`: alphanumerical or hexadecimal input, with or without alphanumerical or hexadecimal echo
- DCON protocol support
- keywords (coil, hreg, asc, hex, etc.) should also be specified from variables
- main menu for all consoles in GUI version
- Modbus register number/address converter utility (in your own scripting language)
- Number converter utility (in your own scripting language)
- modified source code structure of XModshell
- new command `chkdevlock`/`rmdevlock` (only *nix systems)
- new command `datatype`
- new command `exist`
- new command `inputmeth`
- new command `macro`
- new command `mbconv`
- new command `mbmon`
- new command `printcolor`(only CLI and TUI)
- new command `runmeth`
- new command `sendmeth`
- new command `tcpcons`, `tcpread`, `tcpwrite`
- new command `udpcons`, `udpread`, `udpwrite`
- new commands `ioread` and `iowrite`
- new menu items in the main menu for quick execution of Modbus R/W commands
- new menu items for show and edit all register's value in a big table
- new serial baudrates: 150, 300, 600 baud
- serial echo server utility for testing connectivity
- serial ModBus traffic monitor utility
- support for variable and constant arrays
- new predefined constants
- syntax highlighter file for applications using GTKSourceView (for example: Builder, Geany, Gedit, Mousepad, Pluma, Scribes), for Notepad++ (Windows only) and Vim/Neovim
- TCP and UPD echo server utilities for testing connectivity.
v0.1-alpha3
Third and last developer test release with the following changes:- New source code directory structure;
- new commands;
- new predefined constants;
- bug fixes;
- GUI (except DOS);
- script syntax highlighting file for MCEdit and Nano.
v0.1-alpha2
Second developer test release with the following changes:- Bug fixes;
- Modbus/ASCII and Modbus/RTU communication;
- handling of constants;
- three predefined constants and
- 28 new command (total: 94);
- script syntax highlighting file for Micro.
v0.1-alpha1
First developer test release is not yet suitable for work, although it is functional, but it can only communicate via Modbus/ASCII. The purpose of this release is to test the program's construction, operation, packaging, and package installation in all supported environments. In addition, the documentation and other files are checked for possible typos and errors. Only a source package will be released.III. Screenshots
ModShell
Normal command line
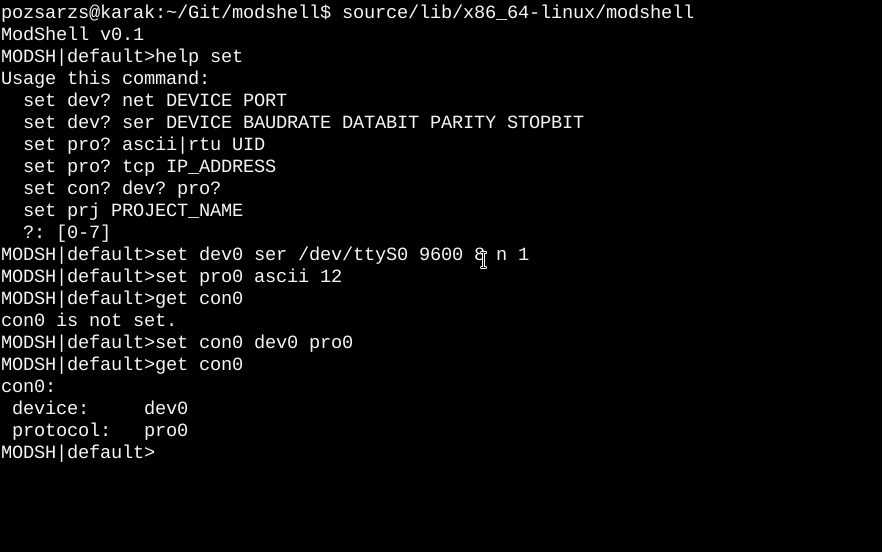
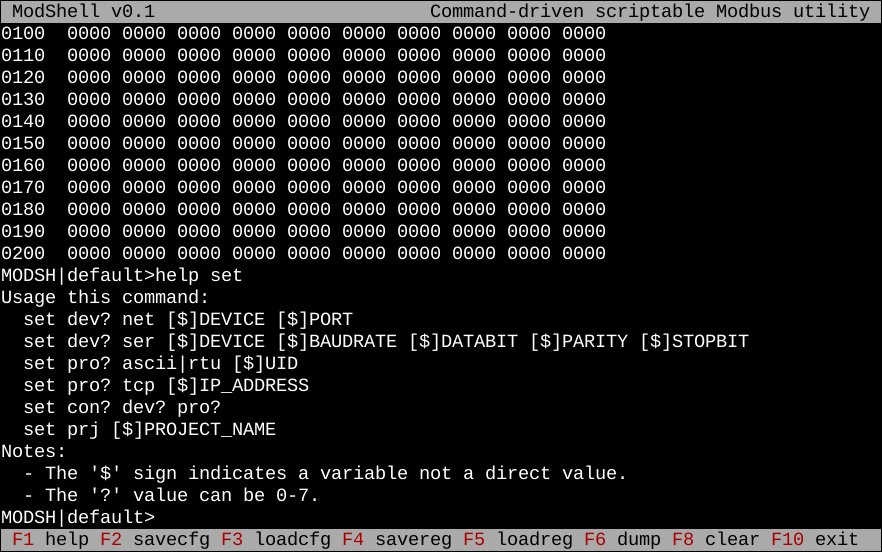
Fullscreen command line
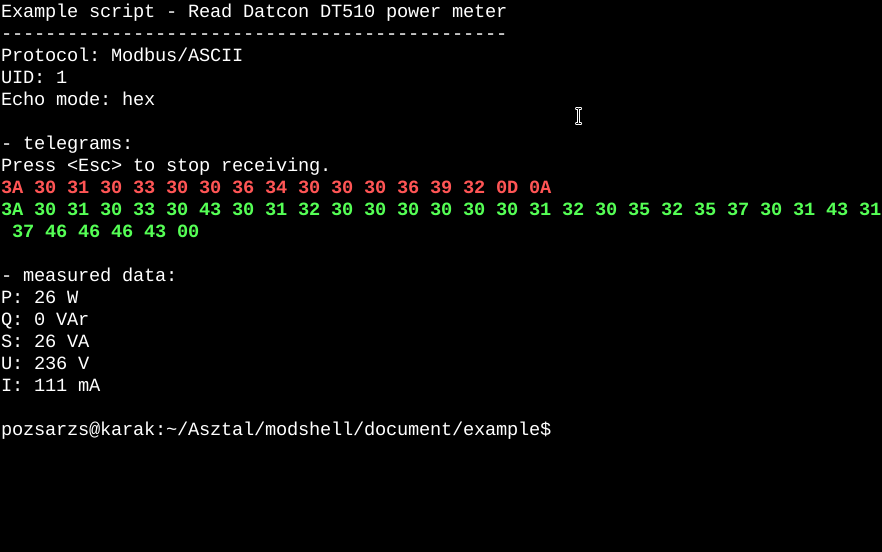
Run example script on bash with ModShell interpreter
XModShell
Dump input registers
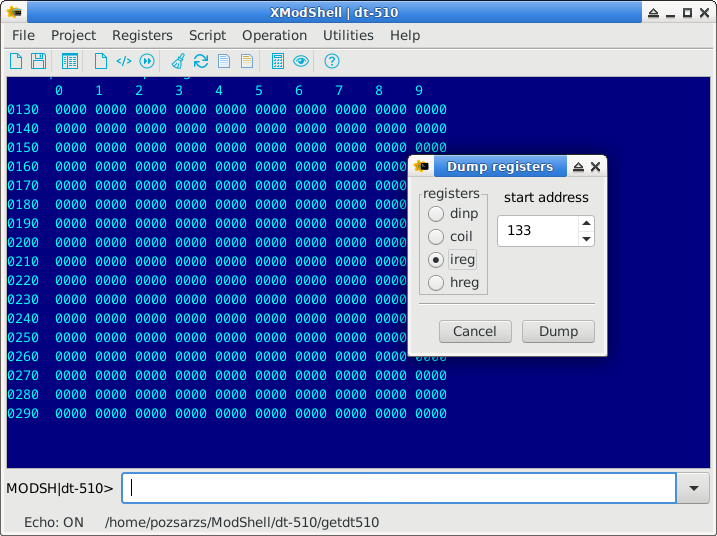
Input registers in Register table
Mini serial console
Script editor
Variable monitor
IV. Used external libraries and programs
- Ararat Synapse Release 40 1
TCP/IP and serial library for FreePascal
Modified BSD style license, Copyright (C) 1999-2012 Lukas Gebauer - Convert - Bin/Oct/Dec/Hex number converter
Unit for Turbo Pascal v3.0
Public Domain, Copyright (C) 1993 Tom Wellige - InpOut32 v1.0.07 Driver Interface DLL 2
Windows Dynamic Link Library (DLL)
Open source/freeware
Copyright (C) 2003-2015 Phil Gibbons
Copyright (C) 2000 - LHelp v2021-02-12 CHM help viewer
Application
GNU GPL v2.0 or later, Copyright (C) 2005-2014 Andrew Haines, Lazarus contributors - ProtCOM v0.1 Protected mode serial port handler for DOS 3
Unit for FreePascal
Creative Common Zero Universal v1.0, Copyright (C) 2024 Pozsar Zsolt
V. About the program in a nutshell
This is a utility that can be used on several operating systems, which can communicate with connected equipment using Modbus/ASCII, Modbus/RTU and Modbus/TCP protocols 4. The basic communication protocol of the program is Modbus, but DCON and HART was also implemented due to communication with other devices. The range of foreign protocols may be expanded later. The program can - even automatically - read, write or copy data from one device to another (e.g. transferring settings). When copying, the source and destination register areas can be different.
The ModShell program has a traditional (CLI) or full-screen (TUI) command-line interface and is also suitable for running pre-created scripts independently (as a command interpreter). The program provides help on the commands that can be used, and offers possible values when the parameters are entered incorrectly. The issued commands are placed in history, which can be browsed with the up/down arrow keys.
The XModShell program has a graphical interface (GUI), which helps to perform several operations with dialog windows, but the original command line input remained available for them (e.g. file selection, settings, etc.) 5.
Operating principle
It must be defined the I/O devices, then the protocols and the connections. There can be eight of each. The data traffic takes place between the preset connections. In all cases, the data is sent to or read from the internal buffer. The size of the buffer is suitable for storing 2*9999 logical and word values of the same size.
128 variables and 32 arrays (which can also be constants) can be created in the program, to which we can assign a value of any type (eg.: string, boolean or integer register value, real number, etc.). Variables and constants can be used to perform logical and arithmetical operations, and can be used to pass values to commands.
It is possible to create 32 single-line macros to replace frequently used longer commands. The program includes 3 pre-created macros, the content of which can also be changed.
Projects
In the program, you can create projects for easier management of settings and data. The name of the current project is shown in the prompt. The project directory will be created in the program directory on DOS, and in the ModShell directory in the user’s home directory on all other systems. If only filename is specified during file operations (without path), this directory will be the source/destination directory.
File operations
The command line history can be exported to a text file and provides it with the appropriate ‘shebang’ for the installation method and operating system. You can easily create a script from this raw file.
Device, protocol and connection settings can be saved and loaded in their own format. During saving, three typed files are created, with the following extensions: DDT, PDT, CDT.
All register values can be saved and loaded in their own format. During saving, two typed files are created, with the following extensions: BDT, IDT.
One or more same type registers can be exported to file. During saving, one text file is created, with CSV, INI or XML extension. The program can only import from INI and XML format files.
We can also create time-stamped log entries with the program and or script.
On exit, the command line history, input and echo mode and colors are preserved.
The program also has basic file and directory management commands.
Script operations
The script on the disc can be loaded into the already running program and started manually.
The loaded script can be edited with a line editor, saved to disk or deleted from the buffer. The graphical version has a simple editor window with syntax highlighting instead of the line editor.
Variables, constants and macros defined before running the script will be deleted. It is also possible to observe the values of up to four variables during runtime and to keep the final valuesof constants and variables created during runtime.
In interpreter mode, operating system command line arguments are available as predefined constants.
Raw serial connection
The program provides the possibility to send and receive raw data via a serial port, and also includes a very simple serial console. The display of sent and received data can be turned off or raw text and hexadecimal viewing can be selected.
Serial connection with DCON protocol
The program also provides the possibility to send and receive data with DCON protocol via a serial port.
Serial connection with HART protocol
The program also provides the possibility to send and receive data with HART protocol via a serial port. A serial/HART gateway may be required for connection.
Raw TCP connection
The program provides the possibility to send and receive raw data via network device with TCP, and also includes a very simple TCP console. The display of sent and received data can be turned off or raw text and hexadecimal viewing can be selected.
Raw UDP connection
The program provides the possibility to send and receive raw data via network device with UDP, and also includes a very simple UDP console. The display of sent and received data can be turned off or raw text and hexadecimal viewing can be selected.
Direct I/O access
The program provides direct, byte-sized reading and writing of hardware I/O ports on PCs and bit-sized reading and writing GPIO ports on Raspberry Pi and Industrial PCs. On Windows operating systems, it uses the included external dynamically linked library.
VI. Implemented commands
| command | category | hotkey | description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | abs |
arithmetic | absolute value | |
| 2 | add |
arithmetic | addition | |
| 3 | avg |
arithmetic | average calculation | |
| 4 | conv |
arithmetic | ALT-C | convert numbers between BIN, DEC, HEX and OCT format |
| 5 | cos |
arithmetic | cosine function | |
| 6 | cotan |
arithmetic | cotangent function | |
| 7 | dec |
arithmetic | decrement integer | |
| 8 | div |
arithmetic | division | |
| 9 | exp |
arithmetic | natural exponential | |
| 10 | idiv |
arithmetic | integer division | |
| 11 | imod |
arithmetic | modulus division | |
| 12 | inc |
arithmetic | increment integer | |
| 13 | inrange |
arithmetic | check the value is in the range | |
| 14 | ln |
arithmetic | natural logarithm | |
| 15 | mul |
arithmetic | multiplication | |
| 16 | mulinv |
arithmetic | multiplicative inverse | |
| 17 | odd |
arithmetic | odd or event | |
| 18 | pow2 |
arithmetic | exponentiation of two | |
| 19 | pow |
arithmetic | exponentiation | |
| 20 | prop |
arithmetic | propotional value calculation (with zero and span) | |
| 21 | rnd |
arithmetic | create random integer | |
| 22 | round |
arithmetic | round real number | |
| 23 | sin |
arithmetic | sine function | |
| 24 | sqr |
arithmetic | square | |
| 25 | sqrt |
arithmetic | square root | |
| 26 | sub |
arithmetic | substraction | |
| 27 | swp |
arithmetic | swap value of two variables | |
| 28 | tan |
arithmetic | tangent function | |
| 29 | copyreg |
communication | copy one or more remote registers between two connections | |
| 30 | dcon |
communication | read or write data from/to remote device with DCON protocol | |
| 31 | hart |
communication | read or write data from/to remote device with HART protocol | |
| 32 | mbconv |
communication | Modbus register number/address converter | |
| 33 | mbgw |
communication | start internal Modbus gateway | |
| 34 | mbsrv |
communication | start internal Modbus slave/server | |
| 35 | mbmon |
communication | start serial Modbus traffic monitor | |
| 36 | readreg |
communication | ALT-R | read one or more remote registers |
| 37 | sercons |
communication | F7 | mini serial console |
| 38 | serread |
communication | read string from a serial device | |
| 39 | serwrite |
communication | write string to a serial device | |
| 40 | tcpcons |
communication | SHIFT-F7 | mini TCP console |
| 41 | tcpread |
communication | read string over the network using TCP | |
| 42 | tcpwrite |
communication | write string over the network using TCP | |
| 43 | udpcons |
communication | mini UDP console | |
| 44 | udpread |
communication | read string over the network using UDP | |
| 45 | udpwrite |
communication | write string over the network using UDP | |
| 46 | writereg |
communication | ALT-W | write data to one or more remote registers |
| 47 | get |
configuration | ALT-G | get device, protocol, connection, colors, project name and timeout |
| 48 | reset |
configuration | ALT-T | reset device, protocol or connection or reset project name |
| 49 | set |
configuration | ALT-S | set device, protocol, connection, colors, project name and timeout |
| 50 | applog |
file | append a record to log file (LOG) | |
| 51 | exphis |
file | export command line history to file (TXT) | |
| 52 | expreg |
file | ALT-E | export one or more registers to file (CSV, INI, XML) |
| 53 | impreg |
file | ALT-I | import one or more registers from file (INI, XML) |
| 54 | loadcfg |
file | F3 | load settings of device, protocol and connection (?DT) |
| 55 | loadreg |
file | F5 | load all buffer registers from typed file (?DT) |
| 56 | savecfg |
file | F2 | save settings of device, protocol and connection (?DT) |
| 57 | savereg |
file | F4 | save all registers to typed file (?DT) |
| 58 | arrclear |
general | clear content of an array | |
| 59 | arrfill |
general | fill an array with a character | |
| 60 | ascii |
general | show ASCII table | |
| 61 | beep |
general | make a beep with internal speaker | |
| 62 | carr |
general | show all constant arrays with theirs size or define a new one | |
| 63 | cls |
general | F8 | clear screen |
| 64 | const |
general | show all constants with theirs value or define a new one | |
| 65 | cron |
general | loaded script scheduled execution | |
| 66 | datatype |
general | detect type of data | |
| 67 | date |
general | show system date and time | |
| 68 | echometh |
general | F9 | alphanumerical/hexadecimal/none local echo method for connections |
| 69 | exit |
general | F10 | exit |
| 70 | for |
general | loop iteration | |
| 71 | getarrsize |
general | get size of an array | |
| 72 | goto |
general | jump to specified label | |
| 73 | help |
general | F1 | show description or usage of the commands |
| 74 | if |
general | selection statement | |
| 75 | input |
general | input data from console | |
| 76 | inputmeth |
general | SHIFT-F9 | alphanumerical/hexadecimal data input method for connections |
| 77 | label |
general | define label (for goto command) | |
| 78 | let |
general | ALT-L | set value of a register, variable, a constant or an element of array |
| 79 | macro |
general | show all macros with theirs value or define a new one | |
| 80 | pause |
general | waits for a keystroke or specified time | |
| 81 | pipe |
general | use an variable array as a FIFO storage | |
| 82 | printcolor |
general | set temporary foreground and background colors for print in CLI/TUI | |
| 83 | print |
general | ALT-P | print message, value of the variable and register |
| 84 | runmeth |
general | get execution method | |
| 85 | sendmeth |
general | CTRL-F9 | char-to-char or string data send method for connections |
| 86 | setarrsize |
general | set size of an array | |
| 87 | stack |
general | use an variable array as a LIFO storage | |
| 88 | var |
general | show all variables with theirs value or define a new one | |
| 89 | varmon |
general | ALT-M | monitoring the value of variables |
| 90 | varr |
general | show all variable arrays with theirs size or define a new one | |
| 91 | ver |
general | show version and build information of this program | |
| 92 | and |
logic | AND logical operations | |
| 93 | bit |
logic | value of the specified bit | |
| 94 | not |
logic | NOT logical operations | |
| 95 | or |
logic | OR logical operations | |
| 96 | roll |
logic | roll bit of integer to left | |
| 97 | rolr |
logic | roll bit of integer to right | |
| 98 | shl |
logic | bit shift to left | |
| 99 | shr |
logic | bit shift to right | |
| 100 | xor |
logic | XOR logical operations | |
| 91 | dump |
register | F6 | dump all registers in binary/hexadecimal format to a table |
| 92 | edit |
script | SHIFT-F4 | edit loaded script with line editor |
| 93 | erasescr |
script | SHIFT-F8 | erase script from buffer |
| 104 | list |
script | F11 | list loaded script |
| 105 | loadscr |
script | SHIFT-F3 | load ModShell scriptfile from disc |
| 106 | run |
script | F12 | run loaded script |
| 107 | savescr |
script | SHIFT-F2 | save loaded script to disc |
| 108 | chr |
string | convert byte to char | |
| 109 | concat |
string | concatenate strings | |
| 110 | length |
string | length of string | |
| 111 | lowcase |
string | conversion to lowercase | |
| 112 | mkcrc |
string | make CRC value | |
| 113 | mklrc |
string | make LRC value | |
| 114 | ord |
string | convert char to byte | |
| 115 | strdel |
string | delete specified element(s) of the string | |
| 116 | strfind |
string | find specified element in the string | |
| 117 | strins |
string | insert element into string | |
| 118 | stritem |
string | specified element of the string | |
| 119 | strrepl |
string | replace element in the string | |
| 120 | upcase |
string | conversion to uppercase | |
| 121 | cd |
system | change actual directory | |
| 122 | chkdevlock |
system | check device lock file | |
| 123 | copy |
system | copy file | |
| 124 | del |
system | remove file | |
| 125 | dir |
system | list directory content | |
| 126 | exist |
system | existence of a file or directory | |
| 127 | gpioinit |
system | initialize GPIO port | |
| 128 | gpioread |
system | read a bit from a GPIO port | |
| 129 | gpiowrite |
system | write a bit to a GPIO port | |
| 130 | ioread |
system | read a byte from an I/O port | |
| 131 | iowrite |
system | write a byte to an I/O port | |
| 132 | md |
system | make directory | |
| 133 | rd |
system | remove directory | |
| 134 | ren |
system | rename file | |
| 135 | rmdevlock |
system | remove device lock file | |
| 136 | type |
system | type file |
(Commands with function keys (F?) are executed immediately, modifier keys (ALT-?) only make typing easier.)
VII. Predefined things
Predefined variables
| name | value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| $verbose | verbosity level (values: NOTHING | ERROR | ALL) |
Empty and any other variable value are equivalent to ALL.
Predefined constants
| name | value |
|---|---|
| $? | exit value of the commands |
| $ARGx | OS command line arguments (interpreter mode) |
| $ARGCNT | number of the OS command line arguments (interpreter mode) |
| $B01 | 150 (baud) |
| $B03 | 300 (baud) |
| $B06 | 600 (baud) |
| $B1 | 1200 (baud) |
| $B2 | 2400 (baud) |
| $B4 | 4800 (baud) |
| $B9 | 9600 (baud) |
| $B19 | 19200 (baud) |
| $B38 | 38400 (baud) |
| $B57 | 57600 (baud) |
| $B115 | 115200 (baud) |
| $EULER | value of e (2.7182818284590452354) |
| $HOME | user’s home directory |
| $PI | value of Pi (3.1415926535897932385) |
| $PRJDIR | directory of the actual project |
| $PRJNAME | name of the actual project |
| $SQRT2 | value of square root of 2 |
| $SQRT3 | value of square root of 3 |
Predefined macros
| name | value |
|---|---|
| mydev0 | set dev0 set /dev/ttyUSB0 9600 8 n 1 |
| mypro0 | set pro0 rtu 1 |
| mycon0 | set con0 dev0 pro0 |
These macros can also be changed.
VIII. Documentation and Help
Modshell and XModShell has a minimal built-in help which you can access by typing help. Additionally, you can view the manual page from *nix shell (man modshell) or modshell.txt on other systems.
In the graphical version, you can use Help and Online Wiki can be opened directly from the ‘Help’ menu.
IX. Contributing
If you find any bugs, please report them! I am also happy to accept pull requests from anyone. You can use the GitHub issue tracker to report bugs, ask questions, or suggest new features. See CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md for details.
X. Links
Source packages
| name | version |
|---|---|
| main.zip | latest |
| modshell-0.1beta1.tar.gz | v0.1-beta1 |
| modshell-0.1alpha3.tar.gz | v0.1-alpha3 |
| modshell-0.1alpha2.tar.gz | v0.1-alpha2 |
| modshell-0.1alpha1.tar.gz | v0.1-alpha1 |
Binaries and installer packages for several OS and architecture
Not all test versions have binary or installation packages. To download, visit Modshell’s webpage.